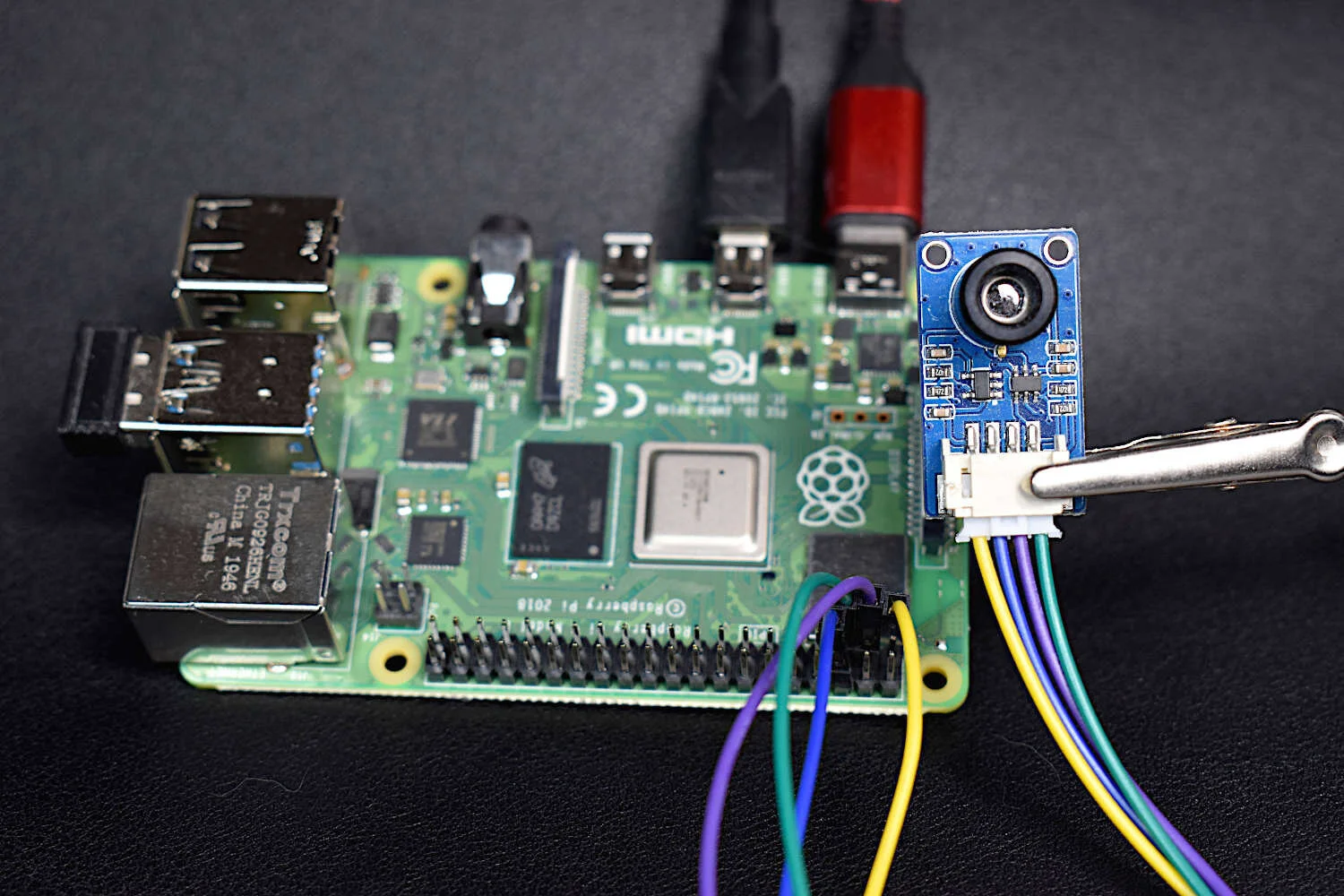
Thermal cameras are similar to standard cameras in that they use light to record images. The most significant distinction is that thermal cameras detect and filter light such that only the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum is recorded, not the visible region [read more about infrared cameras here]. Shortly after the discovery of the relationship between radiation and the heat given off by black bodies, infrared detectors were patented as a way to predict temperature via non-contact instrumentation. In recent decades, as integrated circuits shrink in size, infrared detectors have become commonplace in applications of non-destructive testing, medical device technology, and motion detection of heated bodies. The sensor used here is the MLX90640 [datasheet], which is a 768 pixel (24x32) thermal camera. It uses an array of infrared detectors (and likely filters) to detect the radiation given off by objects. Along with a Raspberry Pi computer, the MLX90640 will be used to map and record fairly high-resolution temeperature maps. Using Python, we will be able to push the RPI to its limits by interpolating the MLX90640 to create a 3 frame-per-second (fps) thermal camera at 240x320 pixel resolution.
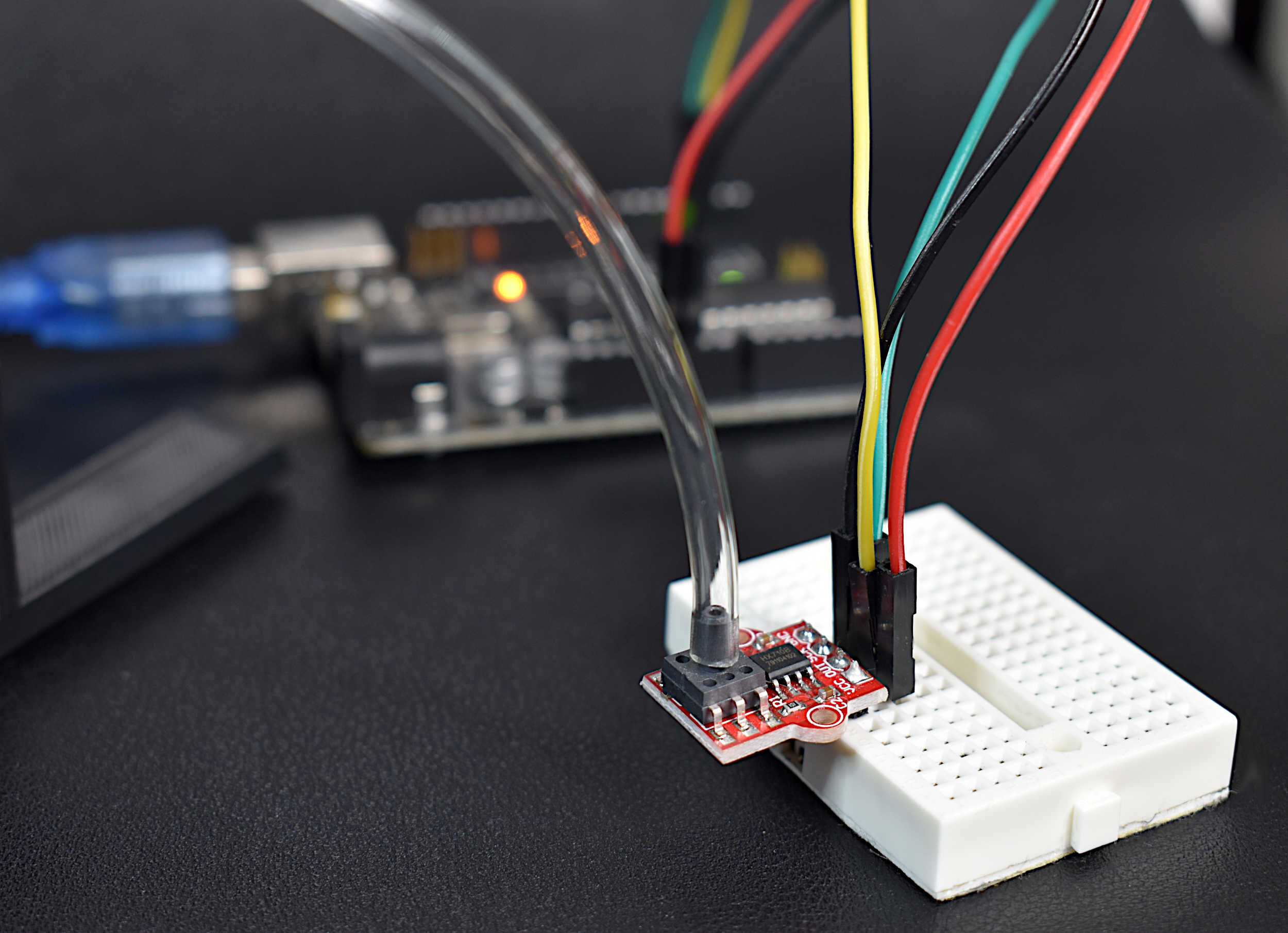
Read MorePressure is defined as an evenly distributed force acting over a surface with a given area. The accurate measurement of pressure is essential for applications ranging from material testing to weighing scales, aircraft altitude prediction, and evaluating biological functions in humans relating to respiration and blood flow In this tutorial, a digital pressure transducer and analog pressure manometer will be used to measure gauge pressure - where the analog manometer is used as the calibration tool for the digital pressure sensor. Arduino will be used to read the digital pressure transducer, an MPS20N0040D, and a 3D printed manometer will be used to measure analog pressure manually.
Read MorePython’s file transfer protocol (FTP) library is used to parse weather station data from the publicly available automated surface observing system (ASOS) from the U.S.A.’s National Climatic Data Center (NCDC). Several programmatic tools available in Python are used to automate the parsing of weather data, as well as visualizing the resulting data.
Read MoreThe NEO-6 is a miniature GPS module designed by u-blox to receive updates from up to 22 satellite on 50 different channels that use trilateration to approximate fixed position of a receiver device every second (or less, for some modules). The particular module used in this tutorial, the NEO-6M, is capable of updating its position every second and communicates with an Arduino board using UART serial communication. The NEO-6M uses the National Marine Electronics Association (NMEA) protocol which provides temporal and geolocation information such as Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), latitude, longitude, altitude, and approximate course speed. The NEO-6M and Arduino board will also be paired with an SD module to create a portable logger that acts as a retrievable GPS tracker.
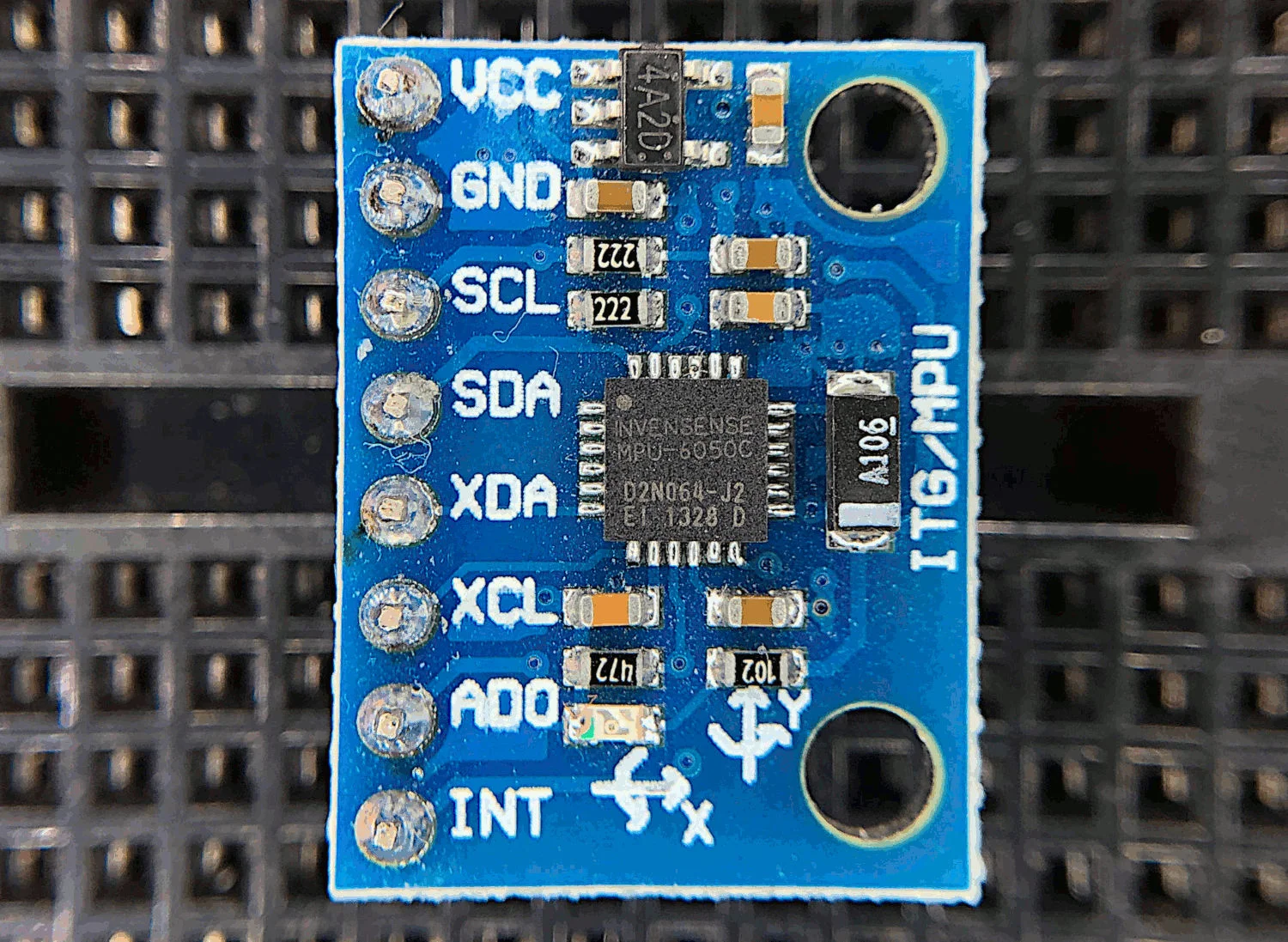
Read MoreThe MPU6050 is a 6-DoF (degree of freedom) accelerometer and gyroscope that is designed for inexpensive, small-scale, and efficient approximation of motion. Accelerometers and gyroscopes are used in smart phones for orientation detection, vibration analysis in vehicles and machines, and even camera stabilization and motion tracking. There are countless applications for accelerometers and gyroscopes, and with devices as accessible as the MPU6050, we can really test the limits of the technology.
Read MoreIn this entry, image processing-specific Python toolboxes are explored and applied to object detection to create algorithms that identify multiple objects and approximate their location in the frame using the picamera and Raspberry Pi. The methods used in this tutorial cover edge detection algorithms as well as some simple machine learning algorithms that allow us to identify individual objects in a frame.
Read MoreTime of flight (ToF) is an approximation of the time it takes a traveling wave to come in contact with a surface and reflect back to the source. Time of flight has applications in automotive obstacle detection, resolving geographic surface composition, and computer vision and human gesture recognition. In the application here, the VL53L1X ToF sensor will be used to track the displacement of a ping pong ball falling down a tube. We can predict the acceleration and behavior of a falling ping pong ball by balancing the forces acting on the ball, and ultimately compare the theory to the actual displacement tracked by the time of flight sensor.
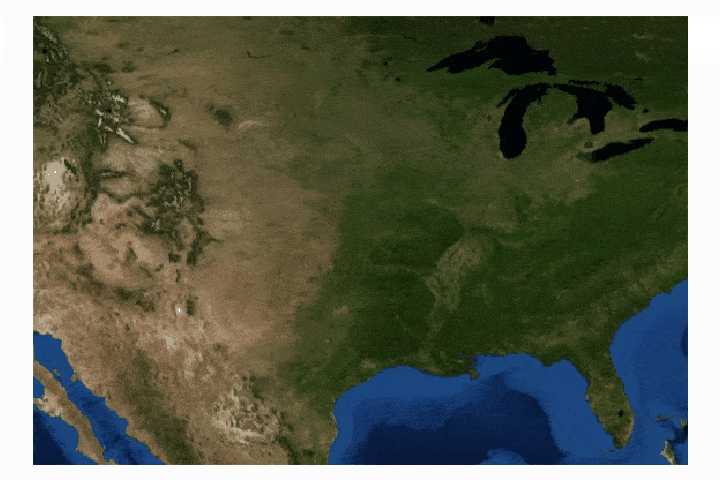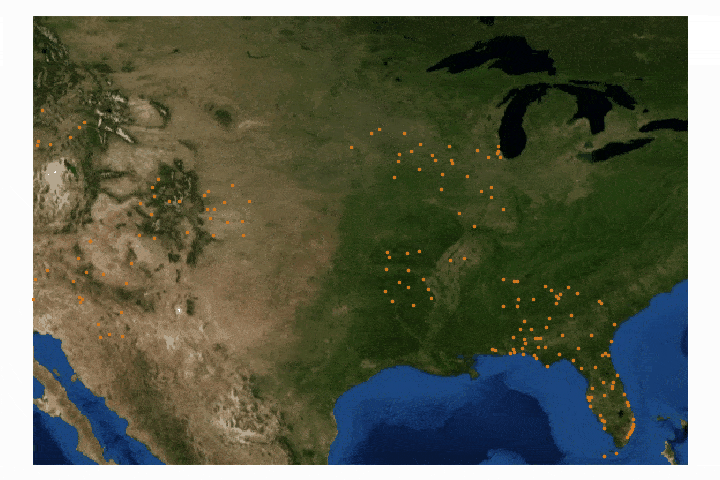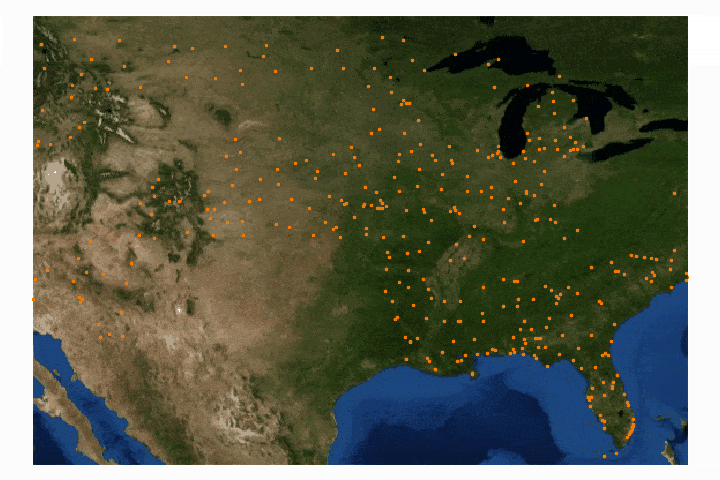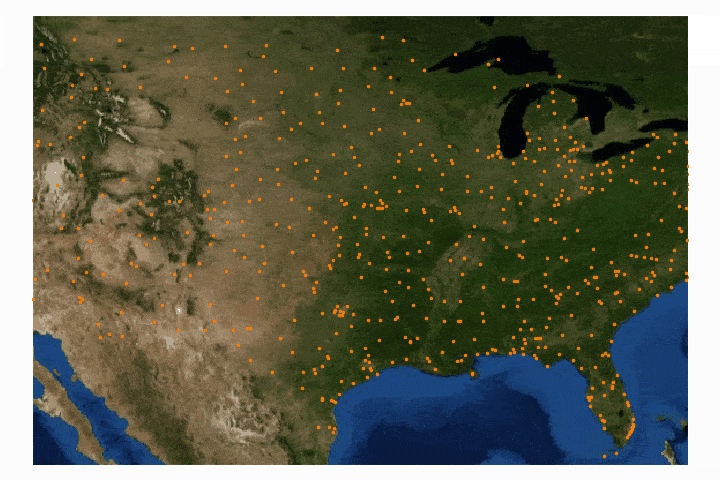
Read MoreGeographic information systems (GIS) are powerful tools used by climatologists, health organizations, defense agencies, real-estate companies, and nearly all professions that rely on location-based data. Geographic data is often very cumbersome to analyze traditionally, which is why visualization tools are essential. Depending on the size and complexity of the data, several robust GIS softwares exist on the market from open-source (free) to paid subscriptions. Each software has its strengths and weaknesses, so depending on the application one software may be more effective than another. A few of the leading softwares are: GE Smallworld, Google Earth Pro, AutoCAD Map 3D, and Maptitude. QGIS is an open-source competitor to ArcGIS, which is arguably the industry leader in the GIS market, so for financial and ease-of-application reasons, QGIS is employed here. I will also cover four scales of geographic analysis: one at the city level (NYC), one at the state level (Washington State), one at the country level (U.S.A.), and one at the world level. The goal is to demonstrate the power and breadth of geographic information systems at any scale.
Read More