Pressure is defined as an evenly distributed force acting over a surface with a given area. The accurate measurement of pressure is essential for applications ranging from material testing to weighing scales, aircraft altitude prediction, and evaluating biological functions in humans relating to respiration and blood flow In this tutorial, a digital pressure transducer and analog pressure manometer will be used to measure gauge pressure - where the analog manometer is used as the calibration tool for the digital pressure sensor. Arduino will be used to read the digital pressure transducer, an MPS20N0040D, and a 3D printed manometer will be used to measure analog pressure manually.
Read MoreTime of flight (ToF) is an approximation of the time it takes a traveling wave to come in contact with a surface and reflect back to the source. Time of flight has applications in automotive obstacle detection, resolving geographic surface composition, and computer vision and human gesture recognition. In the application here, the VL53L1X ToF sensor will be used to track the displacement of a ping pong ball falling down a tube. We can predict the acceleration and behavior of a falling ping pong ball by balancing the forces acting on the ball, and ultimately compare the theory to the actual displacement tracked by the time of flight sensor.
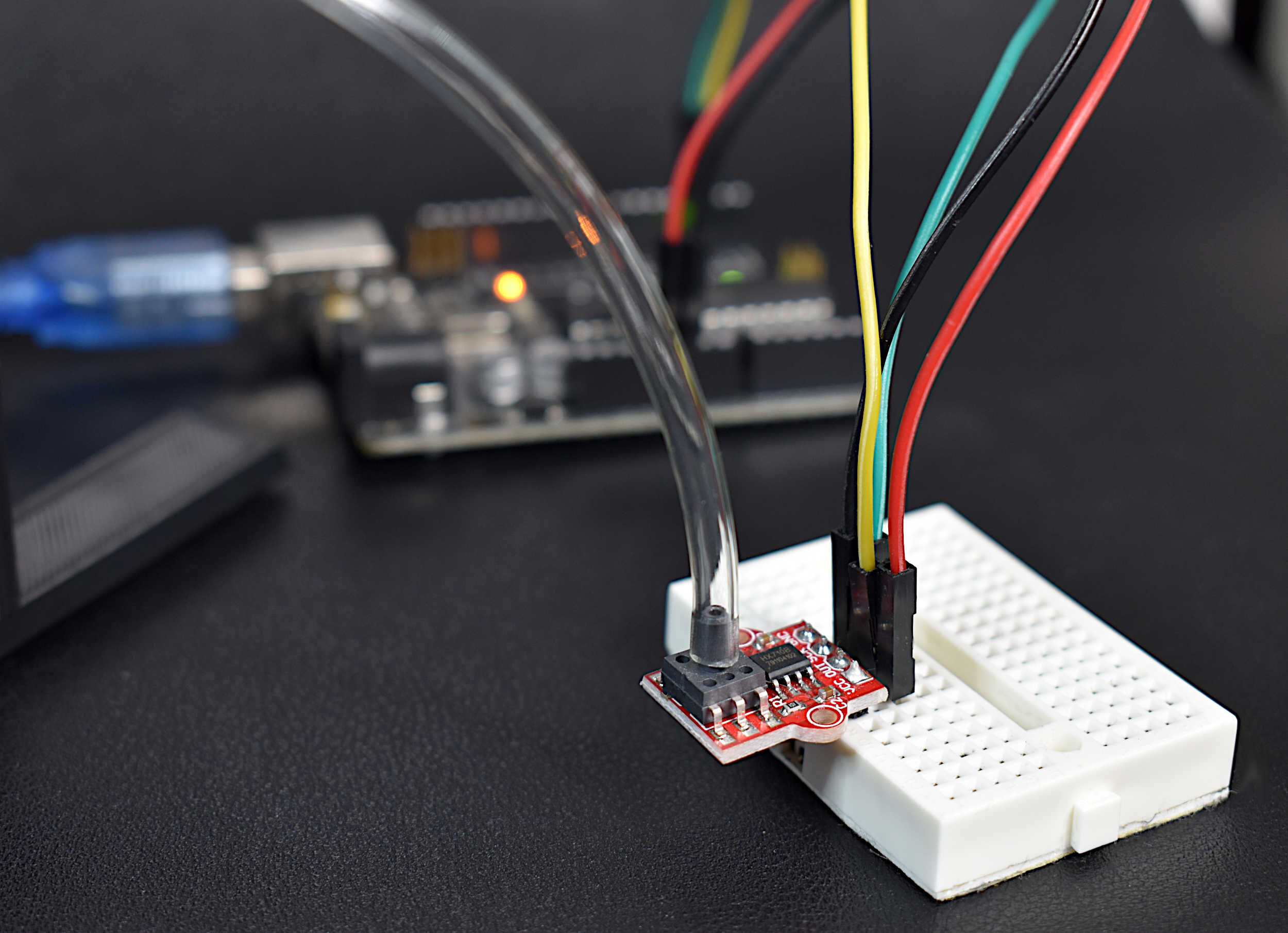
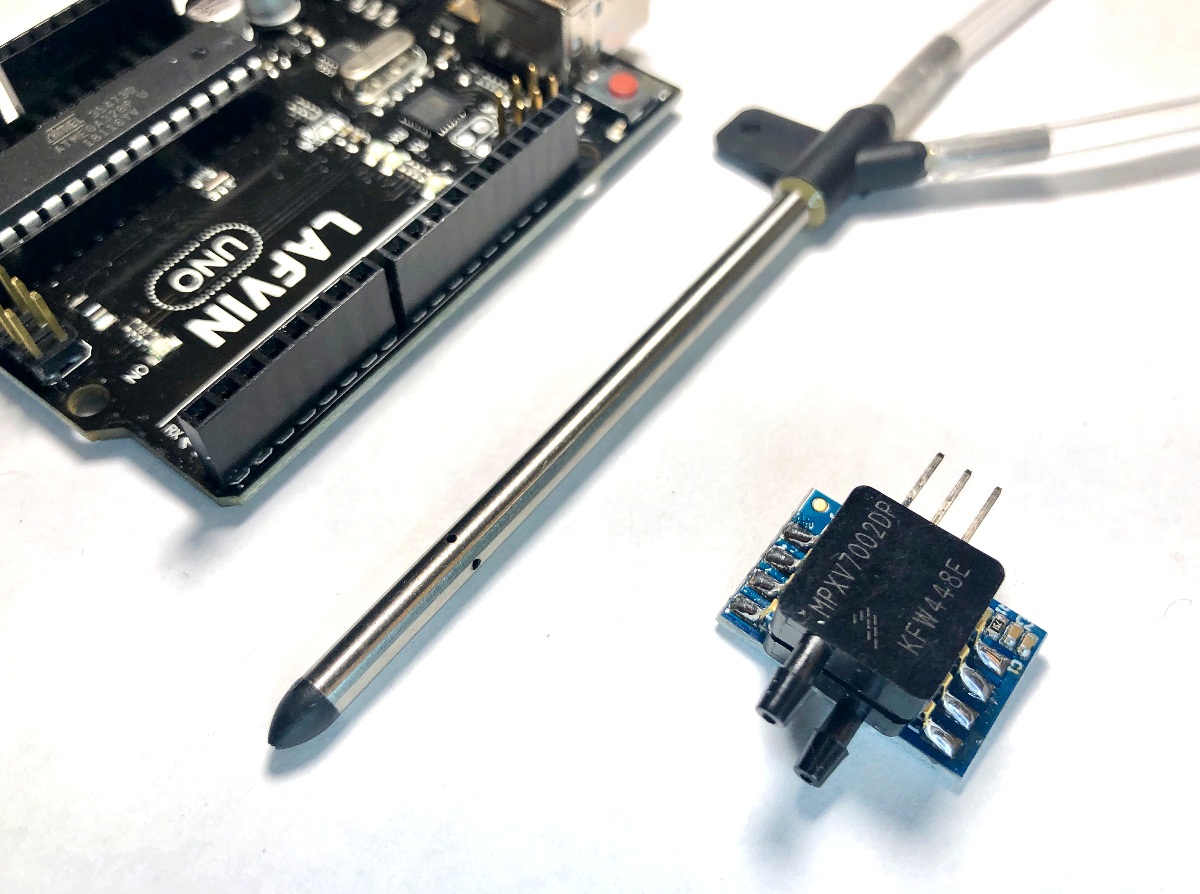
Read MoreThe pitot tube is a device used to approximate the speed of vehicles traveling by air and water. An in-depth article on NASA's website is dedicated to pitot tubes (also called pitot-static tubes, Prandtl tubes), where it cites the primary application as airspeed indicator on aircraft. For more information on design and limitations of the instrument, I recommend perusing that page. For this tutorial, only the basic theory is explored using Bernoulli's equation and a practical application. An inexpensive pitot tube and a digital differential pressure sensor are used to measure pressure, which is converted to a digital signal using an Arduino board.
Read More