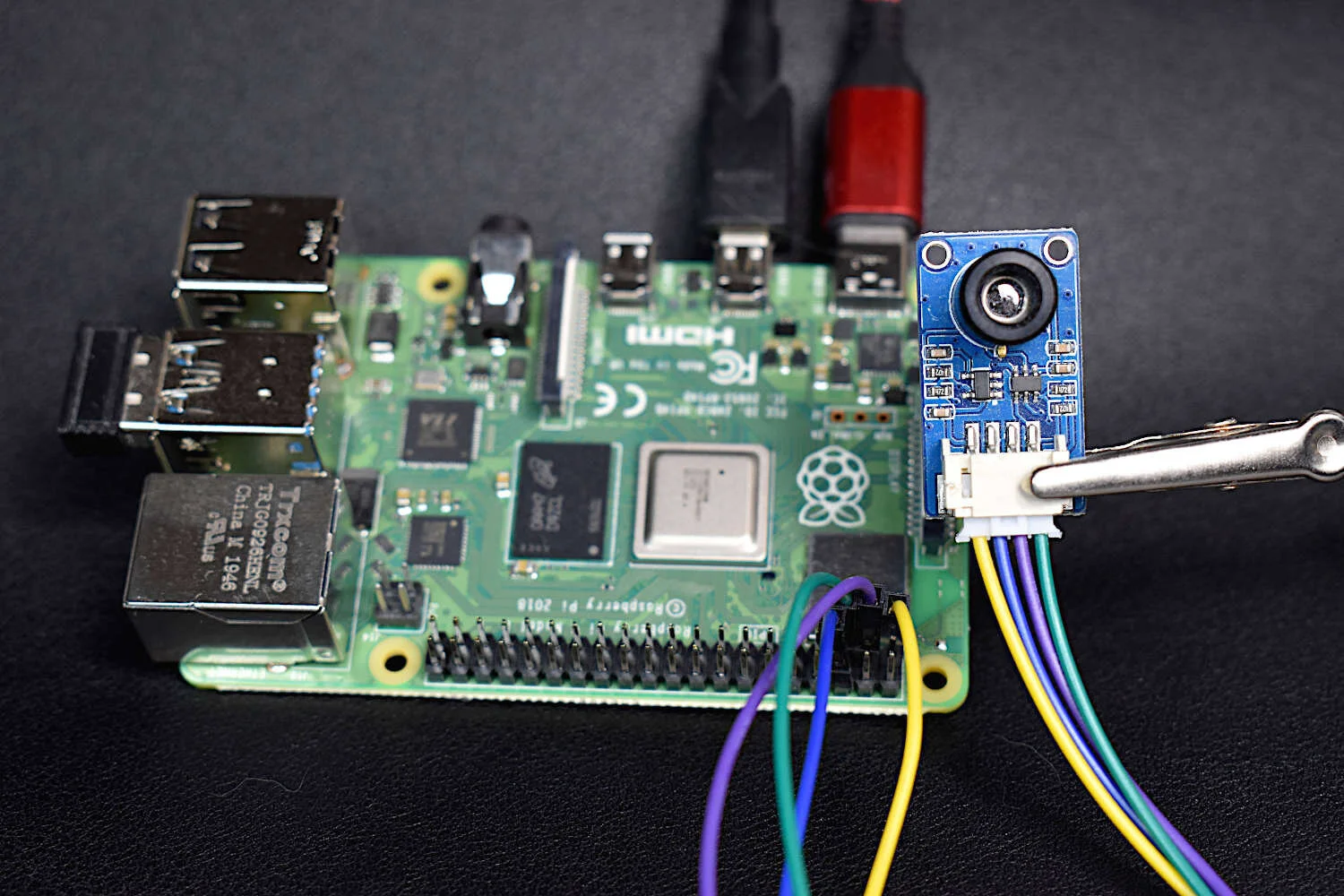
Thermal cameras are similar to standard cameras in that they use light to record images. The most significant distinction is that thermal cameras detect and filter light such that only the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum is recorded, not the visible region [read more about infrared cameras here]. Shortly after the discovery of the relationship between radiation and the heat given off by black bodies, infrared detectors were patented as a way to predict temperature via non-contact instrumentation. In recent decades, as integrated circuits shrink in size, infrared detectors have become commonplace in applications of non-destructive testing, medical device technology, and motion detection of heated bodies. The sensor used here is the MLX90640 [datasheet], which is a 768 pixel (24x32) thermal camera. It uses an array of infrared detectors (and likely filters) to detect the radiation given off by objects. Along with a Raspberry Pi computer, the MLX90640 will be used to map and record fairly high-resolution temeperature maps. Using Python, we will be able to push the RPI to its limits by interpolating the MLX90640 to create a 3 frame-per-second (fps) thermal camera at 240x320 pixel resolution.
Read MorePython’s file transfer protocol (FTP) library is used to parse weather station data from the publicly available automated surface observing system (ASOS) from the U.S.A.’s National Climatic Data Center (NCDC). Several programmatic tools available in Python are used to automate the parsing of weather data, as well as visualizing the resulting data.
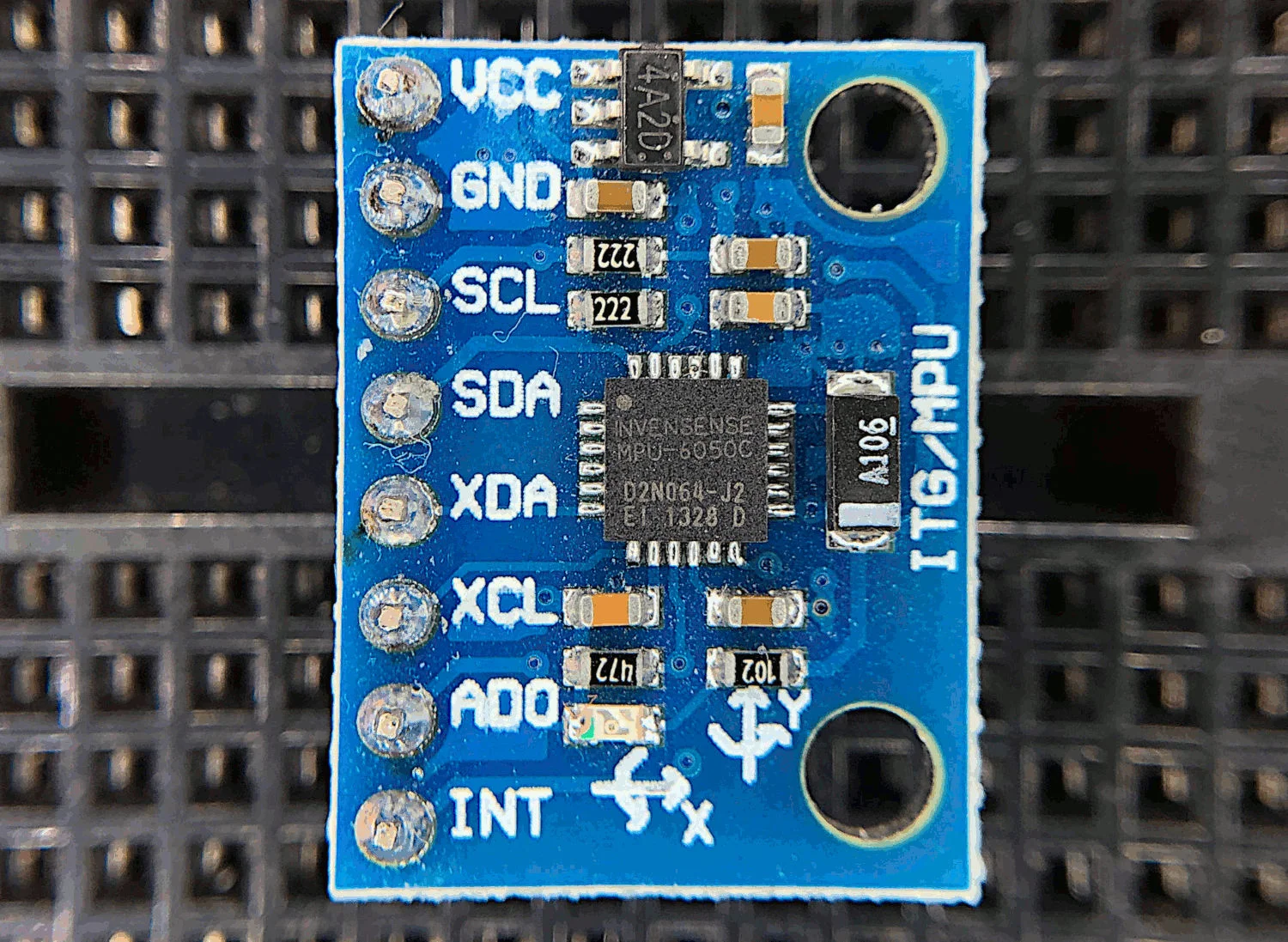
Read MoreThe MPU6050 is a 6-DoF (degree of freedom) accelerometer and gyroscope that is designed for inexpensive, small-scale, and efficient approximation of motion. Accelerometers and gyroscopes are used in smart phones for orientation detection, vibration analysis in vehicles and machines, and even camera stabilization and motion tracking. There are countless applications for accelerometers and gyroscopes, and with devices as accessible as the MPU6050, we can really test the limits of the technology.
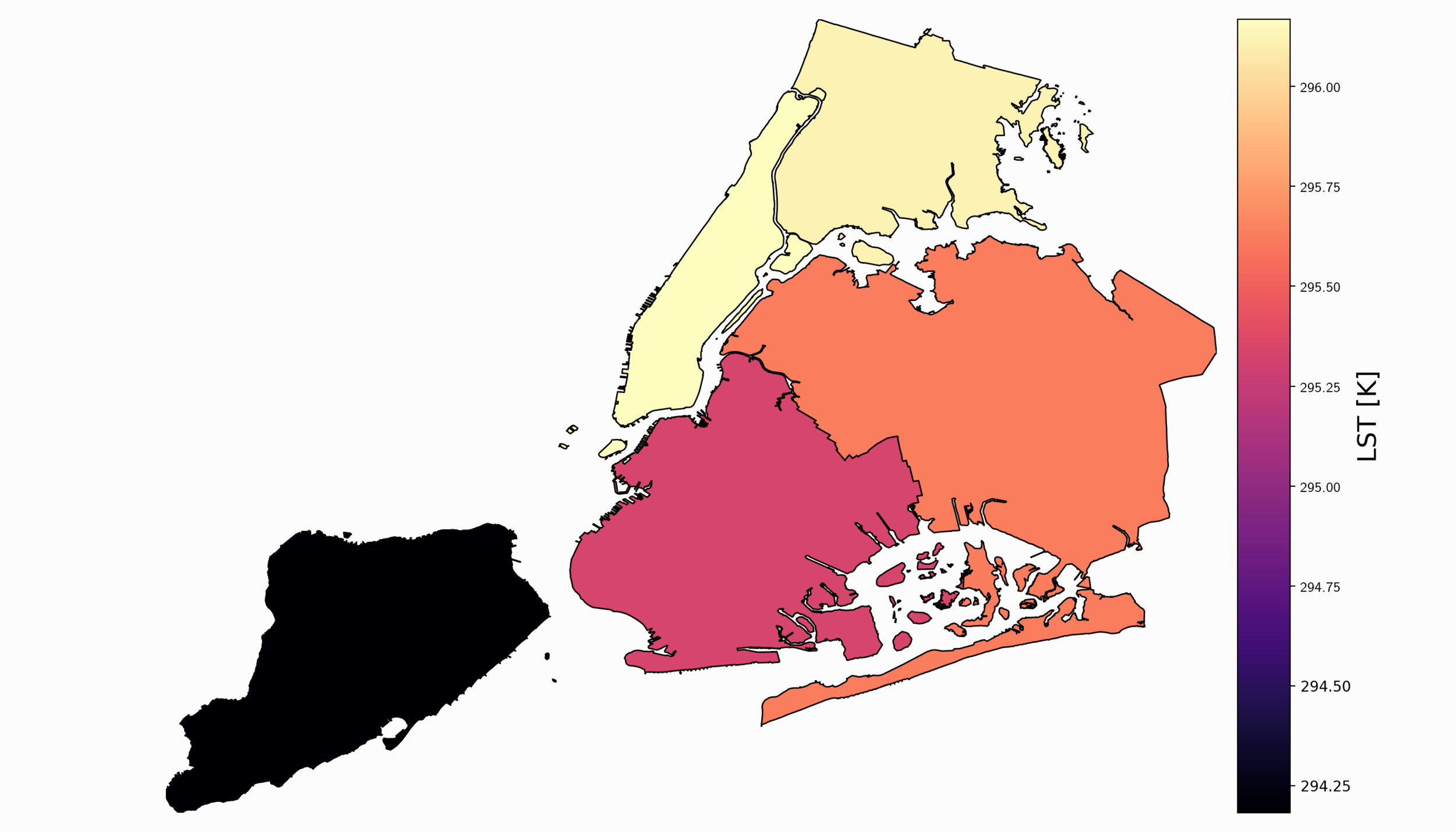
Read MoreFor part II, the focus shifts from the introduction of file formats and libraries to the geospatial analysis of satellite images. Python will again be used, along with many of its libraries. Land Surface Temperature will again be used as the data information, along with shapefiles used for geometric boundary setting, as well as information about buildings and land cover produced by local governments - all of which are used in meteorological and weather research and analyses.
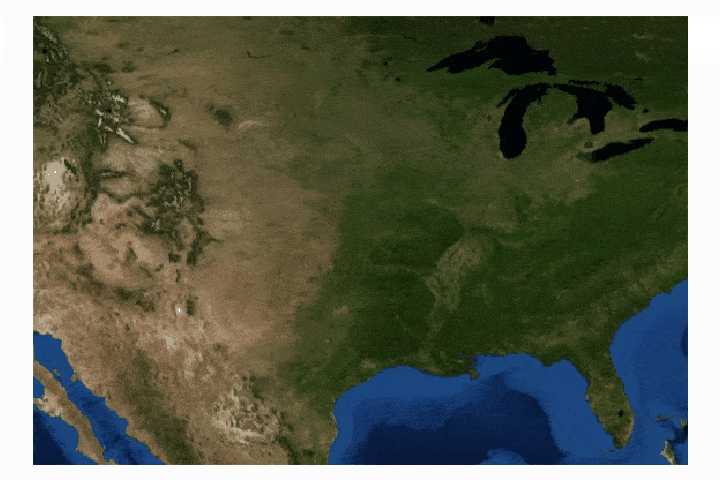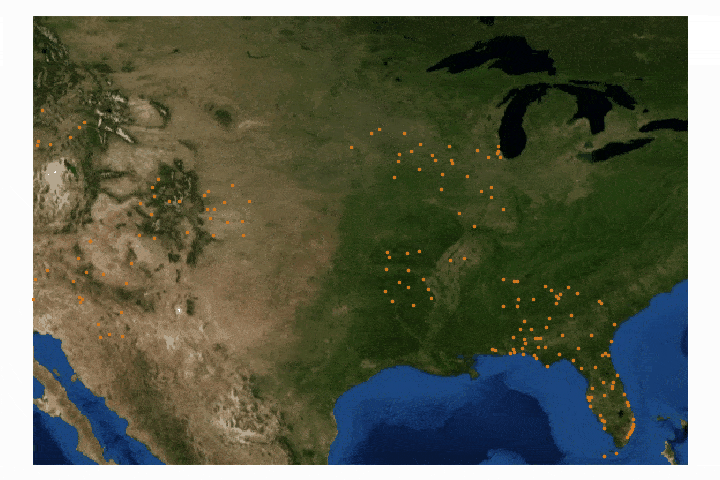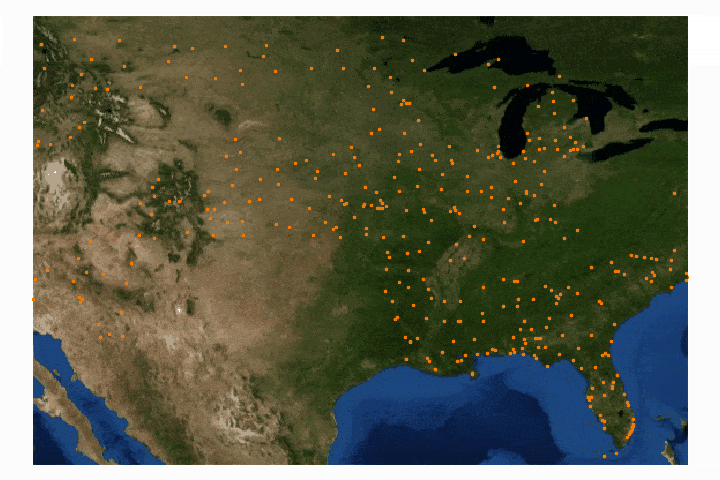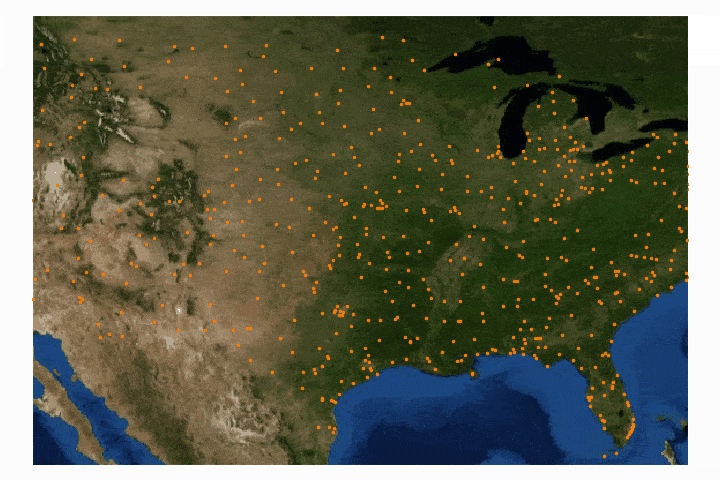
Read MoreIn this tutorial series, Python’s Basemap toolkit and several other libraries are utilized to explore the publicly-available Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-16 (GOES-16). In this first entry, the following will be introduced: acquisition of satellite data, understanding of satellite data files, mapping of geographic information in Python, and plotting satellite land surface temperature (LST) on a map.
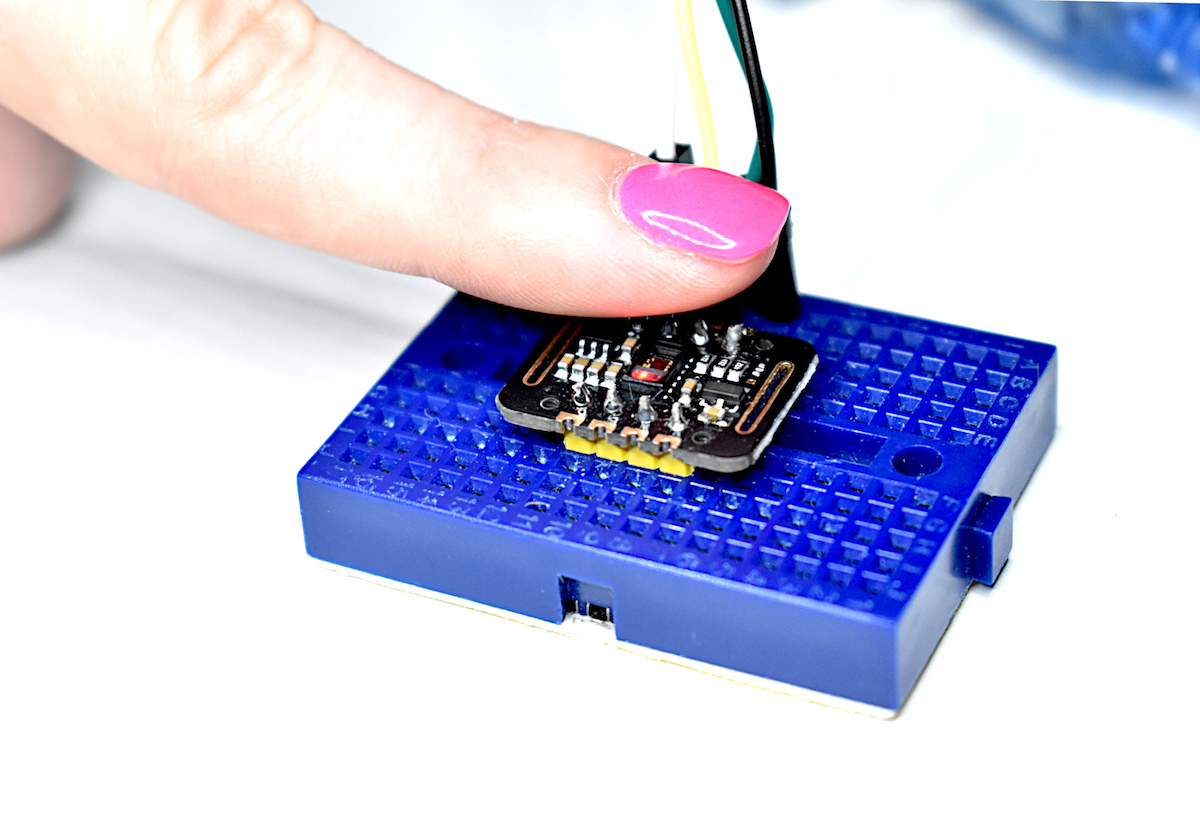
Read MorePulse oximetry monitors the oxygen saturation in blood by measuring the magnitude of reflected red and infrared light [read more about pulse oximetry here and here]. Pulse oximeteters can also approximate heart rate by analyzing the time series response of the reflected red and infrared light . The MAX30102 pulse oximeter is an Arduino-compatible and inexpensive sensor that permits calculation of heart rate using the method described above. In this tutorial, the MAX30102 sensor will be introduced along with several in-depth analyses of the red and infrared reflection data that will be used to calculate parameters such as heart rate and oxygen saturation in blood.
Read More