The TF-Luna is an 850nm Light Detection And Ranging (LiDAR) module developed by Benewake that uses the time-of-flight (ToF) principle to detect objects within the field of view of the sensor. The TF-Luna is capable of measuring objects 20cm - 8m away, depending on the ambient light conditions and surface reflectivity of the object(s) being measured. A vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) is at the center of the TF-Luna, which is categorized as a Class 1 laser, making it very safe for nearly all applications [read about laser classification here]. The TF-Luna has a selectable sample rate from 1Hz - 250Hz, making it ideal for more rapid distance detection scenarios. In this tutorial, the TF-Luna is wired to a Raspberry Pi 4 computer via the mini UART serial port and powered using the 5V pin. Python will be used to configure and test the LiDAR module, with specific examples and use cases.
Read MoreThe QuadMic Array is a 4-microphone array based around the AC108 quad-channel analog-to-digital converter (ADC) with Inter-IC Sound (I2S) audio output capable of interfacing with the Raspberry Pi. The QuadMic can be used for applications in voice detection and recognition, acoustic localization, noise control, and other applications in audio and acoustic analysis. The QuadMic will be connected to the header of a Raspberry Pi 4 and used to record simultaneous audio data from all four microphones. Some signal processing routines will be developed as part of an acoustic analysis with the four microphones. Algorithms will be introduced that approximate acoustic source directivity, which can help with understanding and characterizing noise sources, room and spatial geometries, and other aspects of acoustic systems. Python is also used for the analysis. Additionally, visualizations will aid in the understanding of the measurements and subsequent analyses conducts in this tutorial.
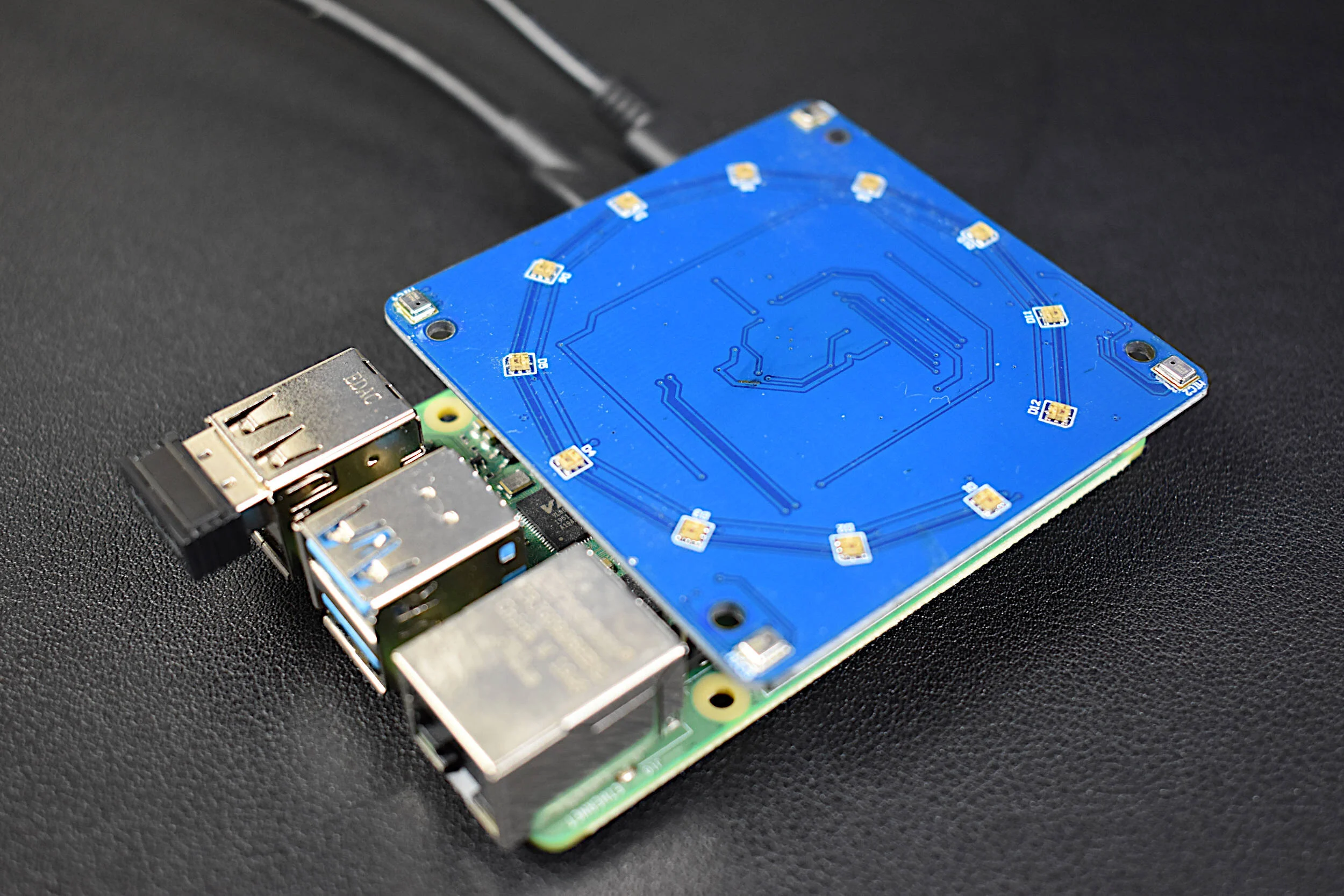
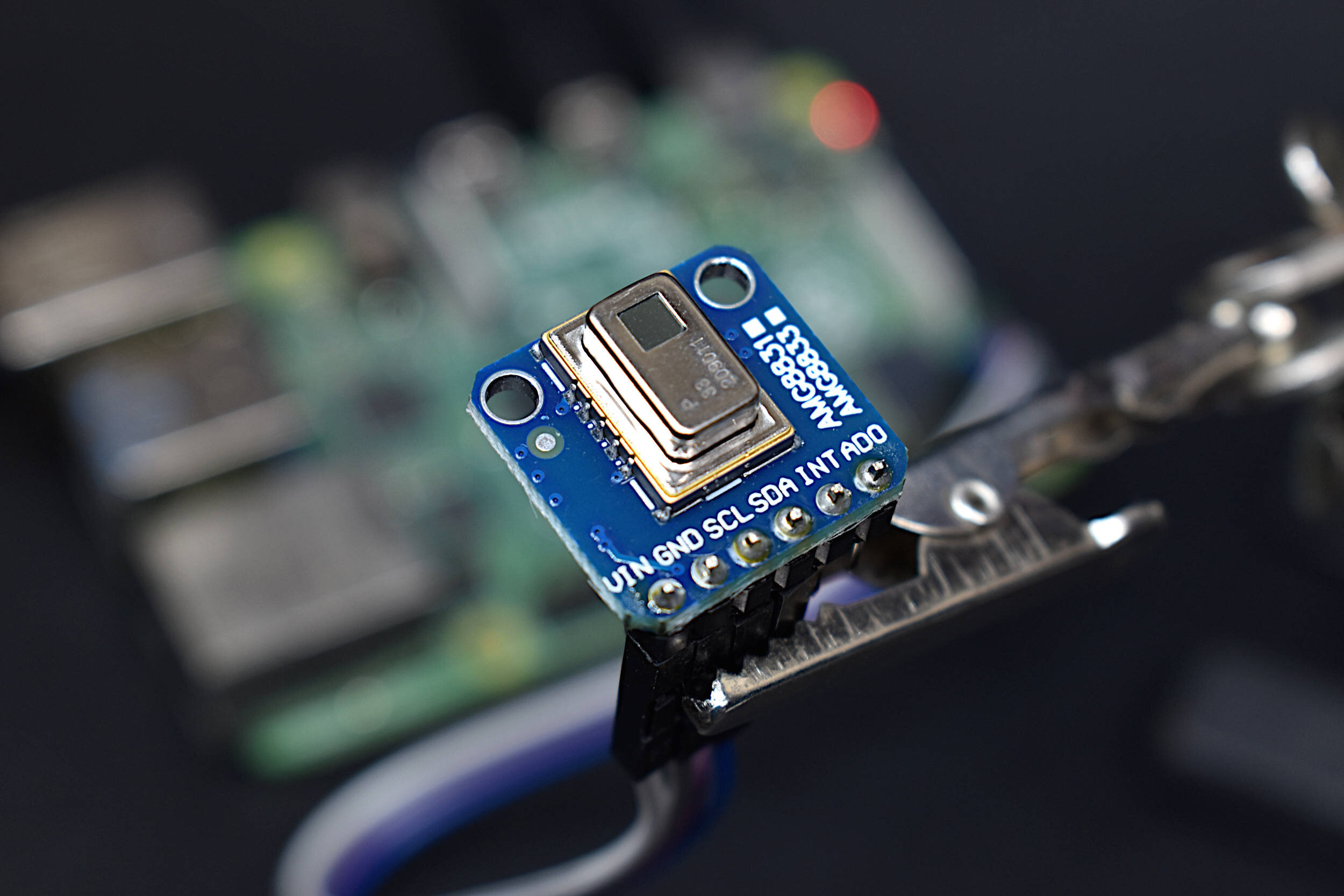
Read MoreThe AMG8833 infrared thermopile array is a 64-pixel (8x8) detector that approximates temperature from radiative bodies. The module is wired to a Raspberry Pi 4 computer and communicates over the I2C bus at 400kHz to send temperature from all 64 pixels at a selectable rate of 1-10 samples per second. The temperature approximation is outputted at a resolution of 0.25°C over a range of 0°C to 80°C. A real-time infrared camera (IR camera) was introduced as a way of monitoring temperature for applications in person counting, heat transfer of electronics, indoor comfort monitoring, industrial non-contact temperature measurement, and other applications where multi-point temperature monitoring may be useful. The approximate error of the sensor over its operable range is 2.5°C, making is particularly useful for applications with larger temperature fluctuations. This tutorial is meant as the first in a series of heat transfer analyses in electronics thermal management using the AMG8833.
Read MoreIn this continuation of the audio processing in Python series, I will be discussing the live frequency spectrum and its application to tuning a guitar. I will introduce the idea of nodes and antinodes of a stringed instrument and the physical phenomena known as harmonics. This will give us a better idea of how to tune the guitar string-by-string and also discern the notes of a given chord - all calculated using the FFT function in Python.
Read More