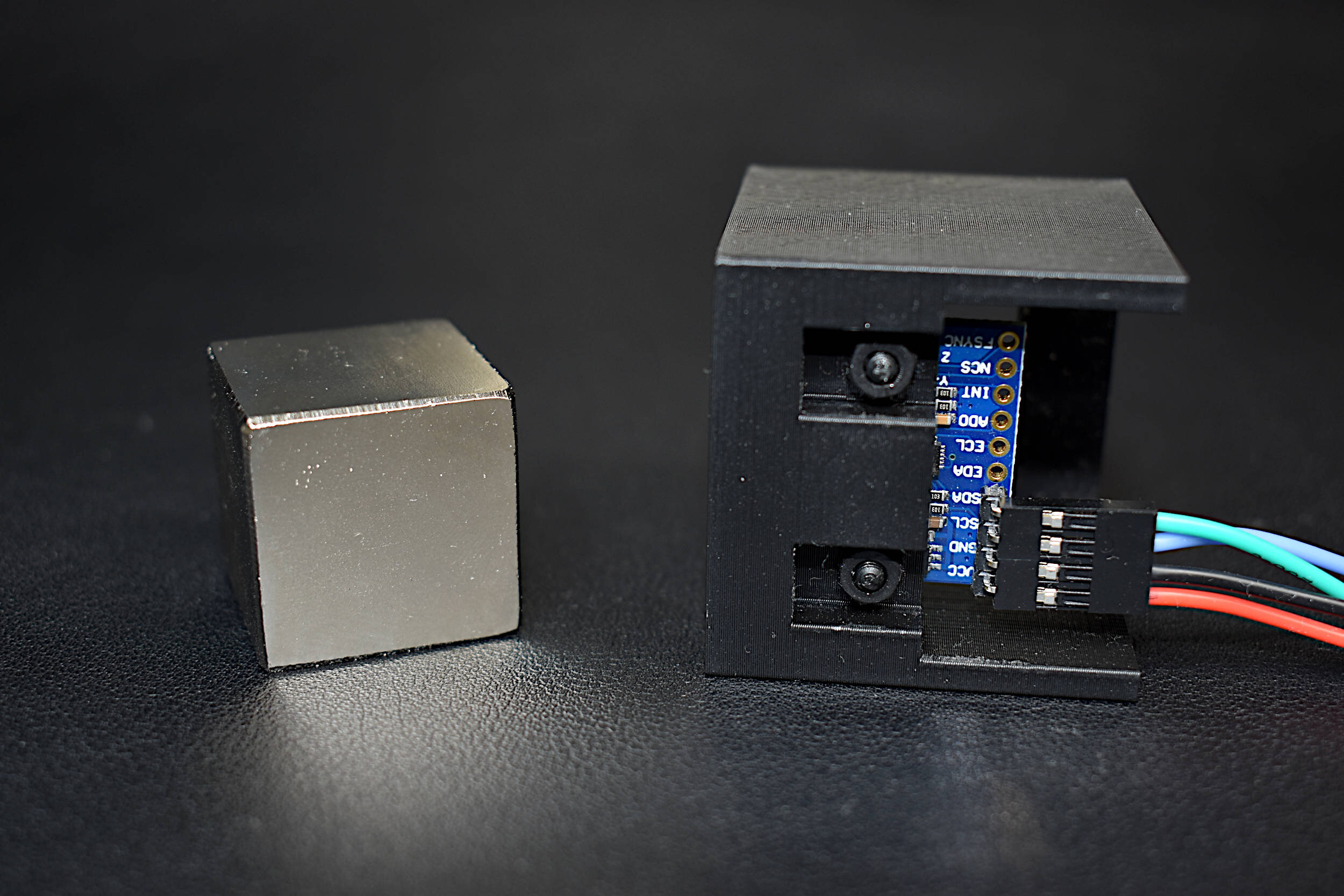
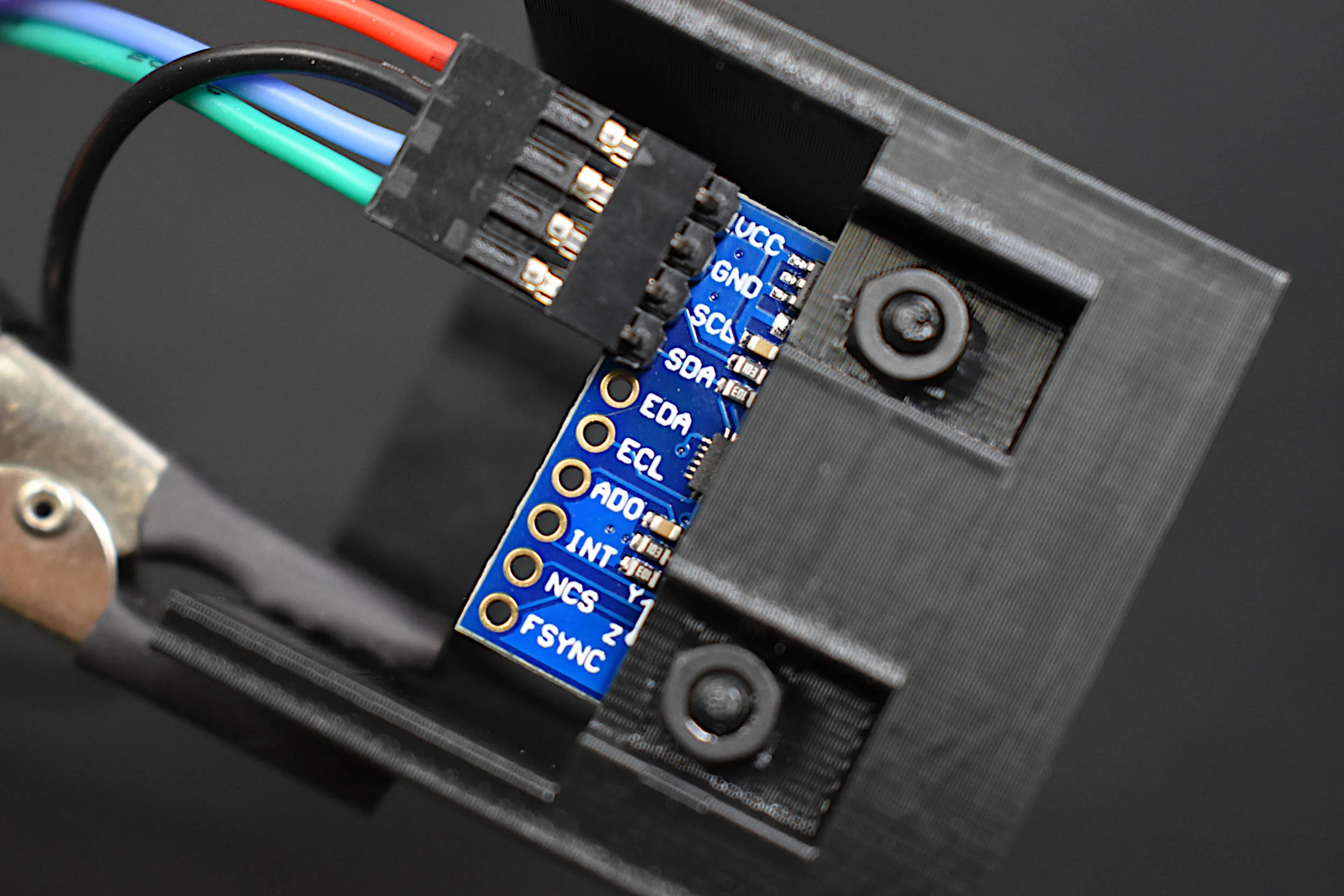
In this tutorial, methods for calibrating a magnetometer aboard the MPU9250 is explored using our Calibration Block. The magnetometer is calibrated by rotating the IMU 360° around each axis and calculating offsets for hard iron effects. Python is again used as the coding language on the Raspberry Pi computer in order to communicate and record data from the IMU via the I2C bus. The second half of this tutorial gives a full calibration routine for the IMU's accelerometer, gyroscope, and magnetometer. The final implementation will allow for moderate (first-order) calibration of the MPU9250 under reasonable conditions, requiring only the calibration block and IMU. Finally, the complete final code will save the coefficients for each sensor for future use in direct applications without the need for constant calibration. The use of the calibration coefficients will allow for improved estimates of orientation, displacement, vibration, and other relevant control and measurement analyses.
Read MoreInertial measurement units (IMUs) can consist of a single sensor or collection of sensors that capture data meant to measure inertial movements in a given reference frame. Acceleration, speed of rotation, and magnetic field strength are examples of sensors contained in an IMU. IMUs can be found in applications ranging smart devices, medical rehabilitation, general robotics, manufacturing control, aviation and navigation, sports learning, and augmented and virtual reality systems. Inertial measurement units have become increasingly popular as their form factors shrink and computational power increases. The ability to use IMUs for indoor/outdoor tracking, motion detection, force estimation, orientation detection, among others has caused the use and availability of inertial sensors to become nearly widespread in smart phones, smart watches, drones, and other common electronic devices. The internet is full of projects involving accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers, but few cover the full calibration of all three sensors. In this project, the manual calibration of a nine degree-of-freedom (9-DoF) IMU is explored. A common MPU9250 IMU is attached to a cube to manually find the calibration coefficients of the three sensors contained within the IMU: accelerometer, gyroscope, and magnetometer. The IMU is wired to a Raspberry Pi - which will allow for high-speed data acquisition rates of all nine components of the IMU.
Read MoreArduino tachometer used to calculate the rotational motion of a part. Tachometers read out revolutions per minute (RPM), which tells the user how often a rotating part completes one full rotation. RPM readings are used in the automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing fields. Tachometers can indicate fuel consumption and motor speed, safety of moving parts, and even wind speed indicators. In this tutorial, the speed of a fan is measured using a hall sensor and neodymium magnet to acquire an accurate depiction of fan speed.
Read More