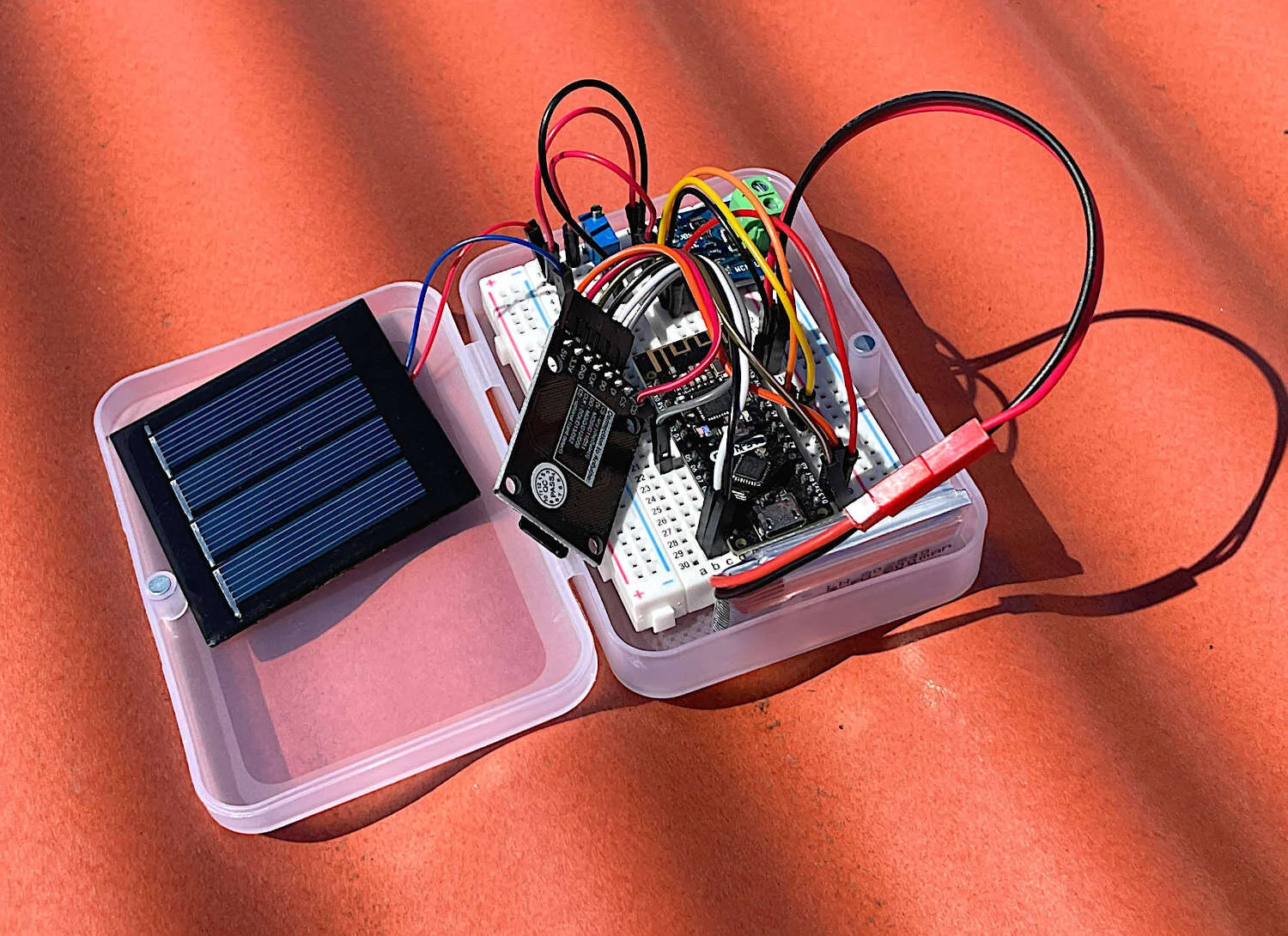
In this tutorial, the aim is to characterize a solar panel by varying the load at (near) peak solar insolation to identify the panel's nominal values such as open-circuit voltage, short-circuit current, max power voltage and current, and max power output. These values help users understand the expectations from a photovoltaic array and how their power needs may be met with a given PV system. An Arduino board will be used to log the current and voltage values outputted from a small solar panel. The current and voltage are measured using a 16-bit analog-to-digital converter power module, the INA226, which will allow us to track the power outputted from the photovoltaic panel. A potentiometer acting as a rheostat will serve as the varying load on the system, which will be used to identify the peak power points of the system. Finally, analyses will be conducted in Python 3, which will allow us to identify the peak power region and also the total power outputted over a duration of 24 hours.
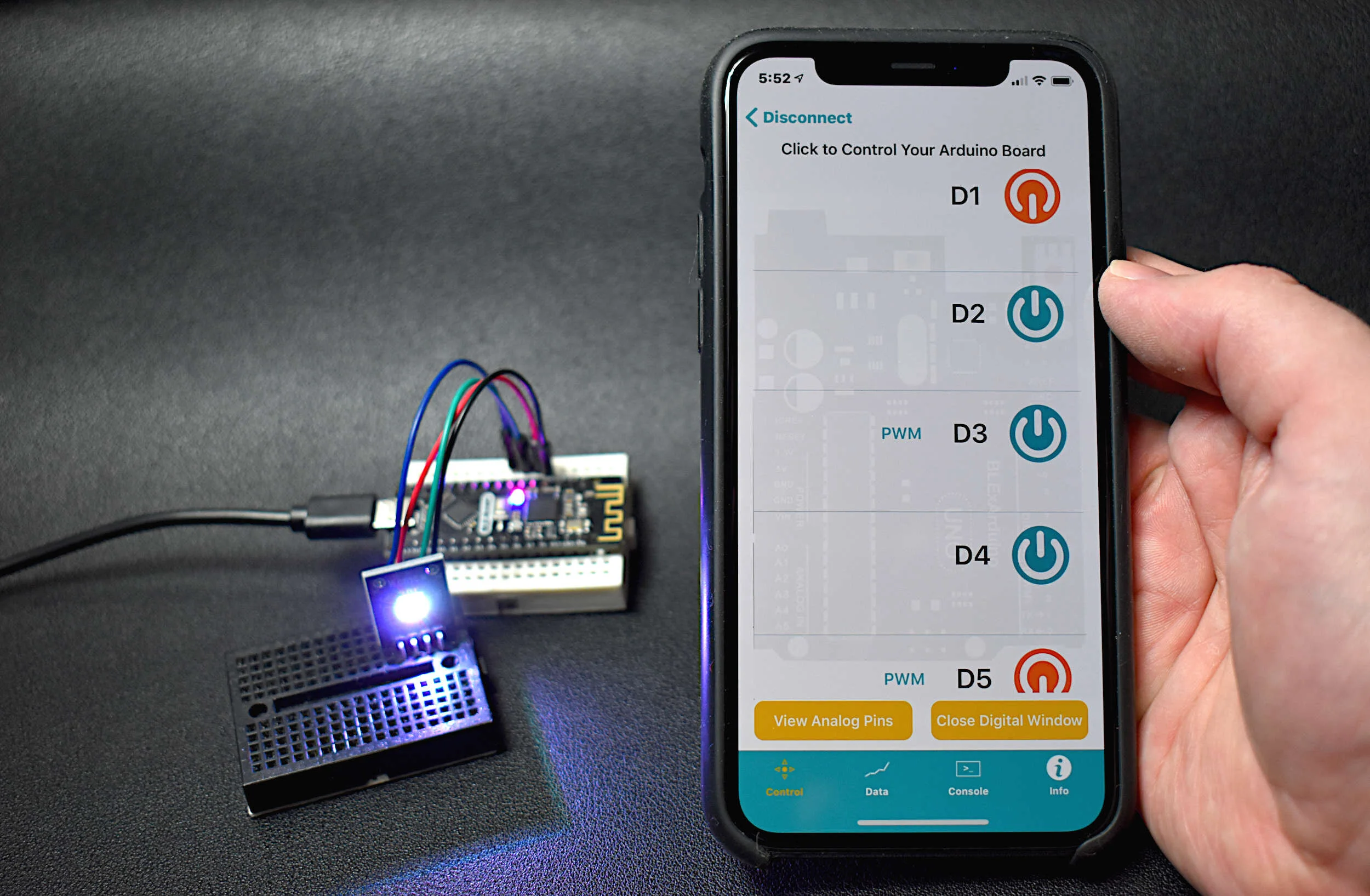
Read MoreThe BLE Nano is introduced as a hybrid between an Arduino Nano and a CC2540 Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) module. The Arduino Nano has an ATmega328P as its main microprocessor, which communicates over the serial port to send and receive Bluetooth packets from the CC2540 BLE chip. This creates a Bluetooth-enabled Arduino device - encased in a Nano-sized circuit board! Using the BLExAR iOS app, the BLE-Nano will be controlled using an iPhone. BLExAR allows users to control the pins on the Nano, which will be demonstrated by switching an RGB LED on and off.
Read More