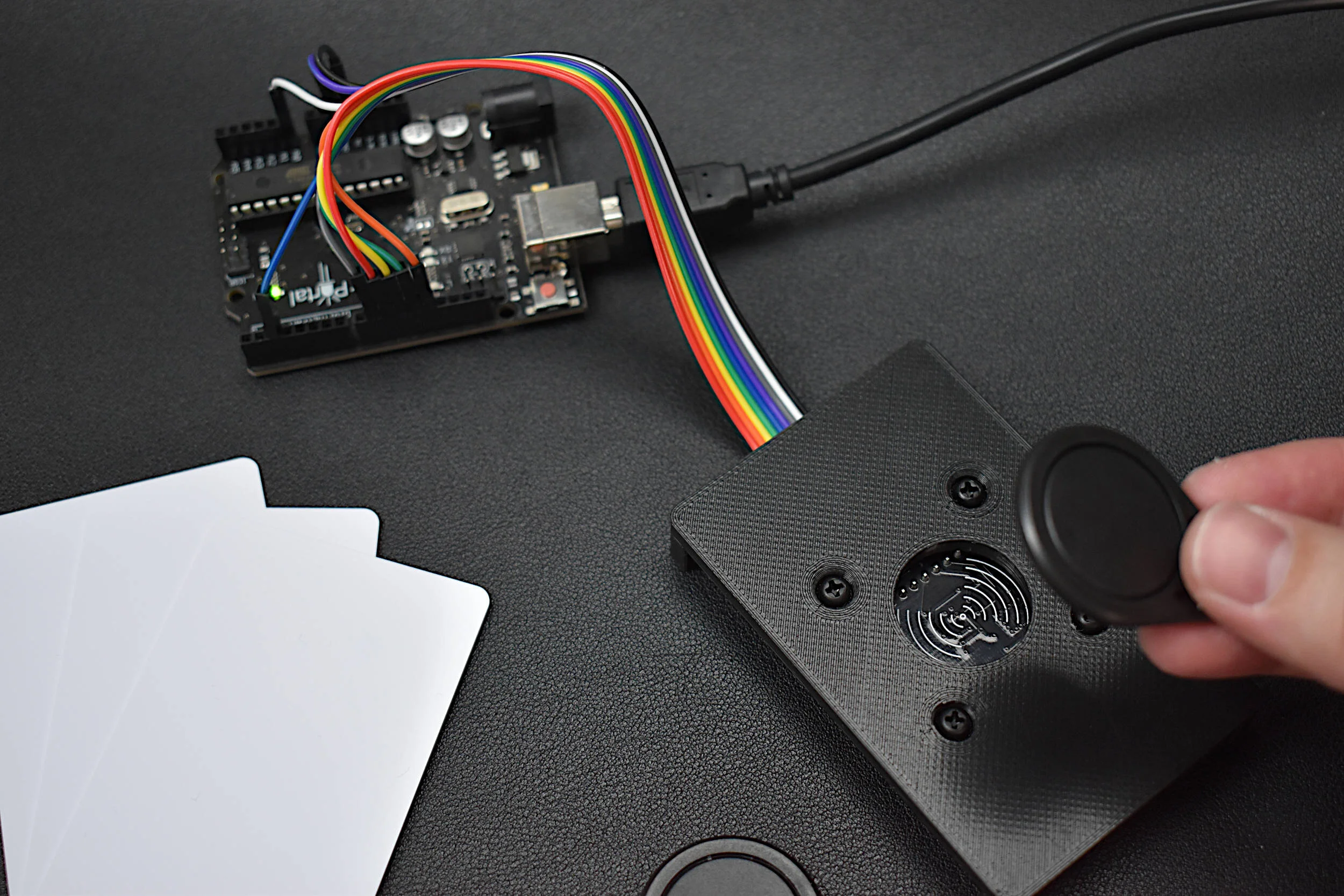
Radio Frequency Identification, or RFID, is a widely used technology developed for storing and retriving information in radio frequency-enabled devices. Most often, RFID systems consist of one or multiple RF tags, an RF reader, and a database. In this tutorial series, passive, high frequency (13.56 MHz) RFID tags are the focus, as they are very compact, inexpensive, and require no external battery power. Using an Arduino board, a common RFID reader (MFRC522), and a few RFID tags/cards, we will be exploring methods for reading and writing RFID information in an attempt to understand the how RFID communication works and the limits of the technology.
Read MoreThis tutorial will explore the range of capabilities available to the Arduino SD library by using a real-world example of data logging. The SD library allows users to read/write, list files, create/remove files, and make/delete directories. Additionally, we will develop an algorithm that creates a new file every time the Arduino board is restarted, which will prevent overwriting of existing data records. The resulting data file will be in comma separated format and contain multiple data points, including a time stamp in milliseconds since the program started. Therefore, it is important to record the program start time. For very accurate time monitoring tasks, a real-time clock is recommended, however, for the experiments conducted here, relative time suffices.
Read More