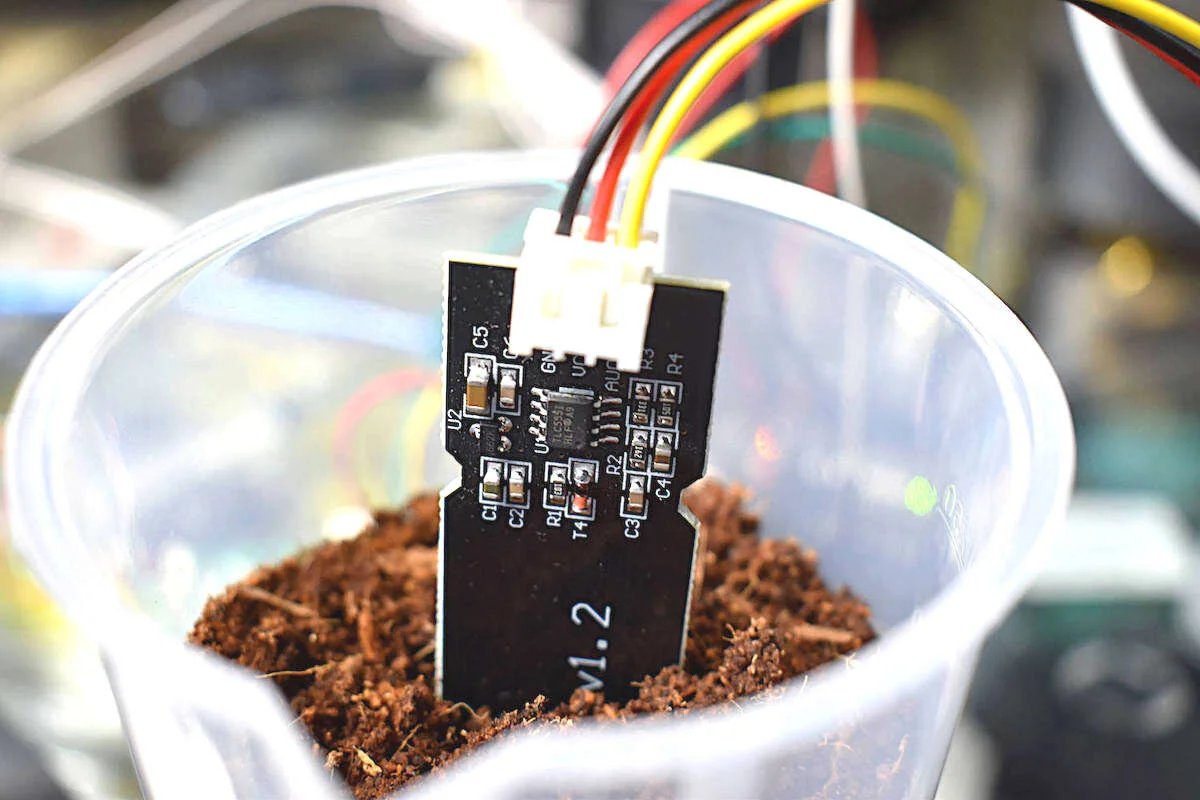
Soil moisture can be measured using a variety of different techniques: gravimetric, nuclear, electromagnetic, tensiometric, hygrometric, among others. The technique explored here uses a gravimetric technique to calibrate a capacitive-type electromagnetic soil moisture sensor. Capacitive soil moisture sensors exploit the dielectric contrast between water and soil, where dry soils have a relative permittivity between 2-6 and water has a value of roughly 80. Accurate measurement of soil water content is essential for applications in agronomy and botany - where the under- and over-watering of soil can result in ineffective or wasted resources. With water occupying up to 60% of certain soils by volume, depending on the specific porosity of the soil, calibration must be carried out in every environment to ensure accurate prediction of water content. Luckily, the accuracy of measurement devices has been increasing while the cost of the sensors have been decreasing. In this experiment, an Arduino board will be used to read the analog signal from the capacitive sensor, which will output voltage values which can be calibrated to volumetric soil moisture content via gravimetric methods.
Read More